IRS-Aided Massive MIMO ISAC System
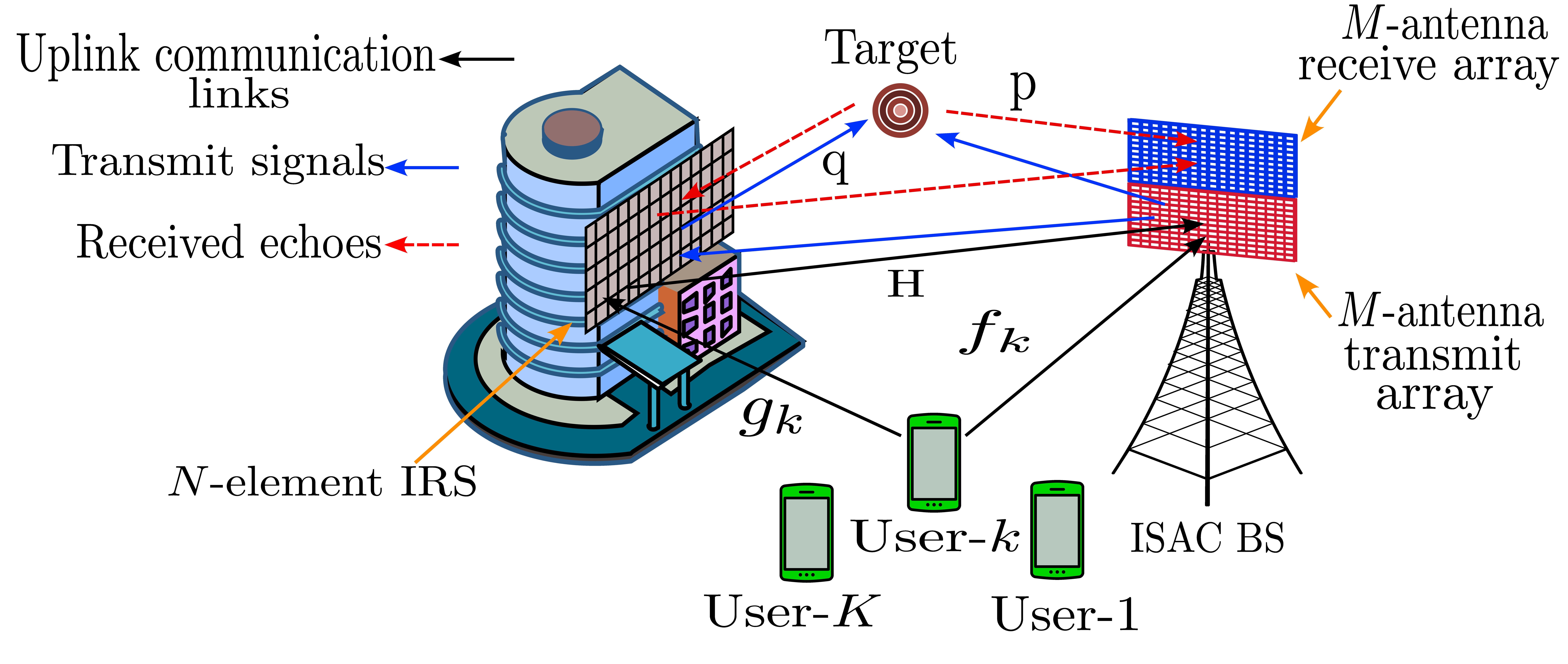
System model
 |
Problem context & motivation
6G will require joint communication and sensing capabilities to support applications such as autonomous driving, industrial automation, and environmental monitoring.
Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRSs) and massive MIMO are promising enablers for ISAC, but most IRS-aided ISAC designs rely on computationally complex non-linear precoding methods.
There is a lack of fundamental performance analysis for IRS-aided massive MIMO ISAC systems with computationally efficient linear precoders.
Main contribution
Proposes and analyzes an IRS-aided massive MIMO ISAC system using maximal ratio transmission (MRT)-based linear precoders for both communication and sensing beams.
Incorporates spatially correlated Ricean fading and imperfect CSI obtained via LMMSE uplink channel estimation.
Derives closed-form achievable user rates for communication and models sensing via a 2D MUSIC-based target localization algorithm.
Optimizes IRS phase-shifts using statistical CSI to maximize the weakest user's average composite channel gain while meeting a minimum sensing channel power constraint.
System model
BS with large uniform planar arrays (UPAs) for transmit and receive.
IRS with UPA of passive elements aiding both communication and sensing.
Single target for sensing, \(K\) single-antenna users for communication.
Composite channels include direct BS-user links and cascaded BS-IRS-user links.
IRS phase-shift optimization
Ojective funtion:
Maximize the minimum average power gain among communication users.
Constraints:
Maintain an average sensing channel power threshold.
Strict modulus constraint
Reformulates the IRS phase-shift design into a convex problem using first-order approximations and solves iteratively via CVX/Gurobi.
Ensures constant-modulus IRS reflection constraints after each iteration.
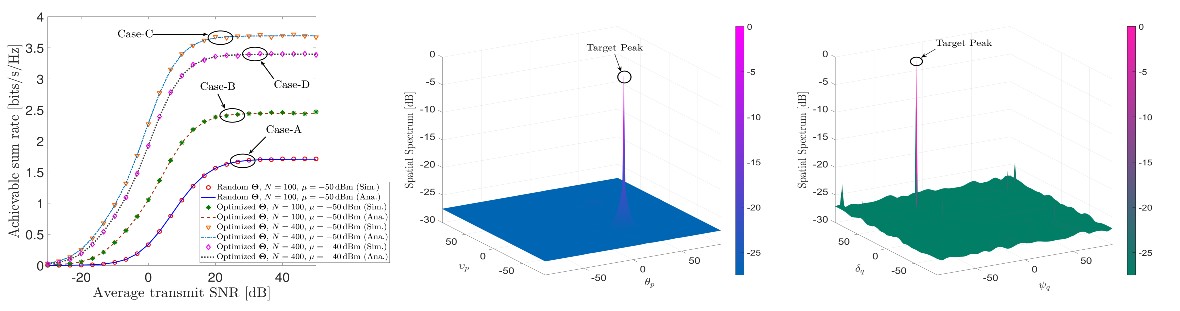
Key numerical results
Optimized IRS phase-shifts yield sum-rate gain over random IRS phase-shifts
Increasing IRS elements provides additional sum-rate gains .
Higher sensing channel power constraints reduce achievable sum rate, demonstrating the sensing-communication trade-off.
MUSIC algorithm accurately recovers target location parameters in all tested scenarios, confirming the sensing capability.
 |
Conclusion
IRS-aided massive MIMO ISAC with simple linear MRT-based precoding can effectively balance sensing and communication trade-offs.
Statistical CSI-based IRS phase-shift optimization offers substantial performance improvements with random counterparts.
References
1. R. Kulathunga, J. K. Dassanayake, and G. Amarasuriya, “IRS-Aided Massive MIMO ISAC Systems,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Commun. (ICC), Montreal, Canada, Jun. 2025.