Cell-Free Massive MIMO-Aided ISAC
System models
 |
Problem context & motivation
Cell-free massive MIMO (CF-mMIMO) is well-established in the literature, however, ISAC incorporated CF-mMIMO research remain at an “embryonic” stage.
Core contribution
Develops a computationally-efficient ISAC framework for CF-mMIMO: each transmit AP uses a linear conjugate precoder (based on its own uplink CSI) to design a superimposed ISAC waveform.
Derives closed-form achievable downlink rates and signal-to-clutter-plus-noise ratio (SCNR).
Proposes a max-min power-allocation algorithm that meets per-AP power and a predefined signal-to-clutter-plus-noise (SCNR) ratio.
Analyzes communication and sensing performance in terms of achievable rate and 2-D MUSIC spectrum, explicitly accounting for spatially correlated Rician fading, imperfect CSI, and clutter.
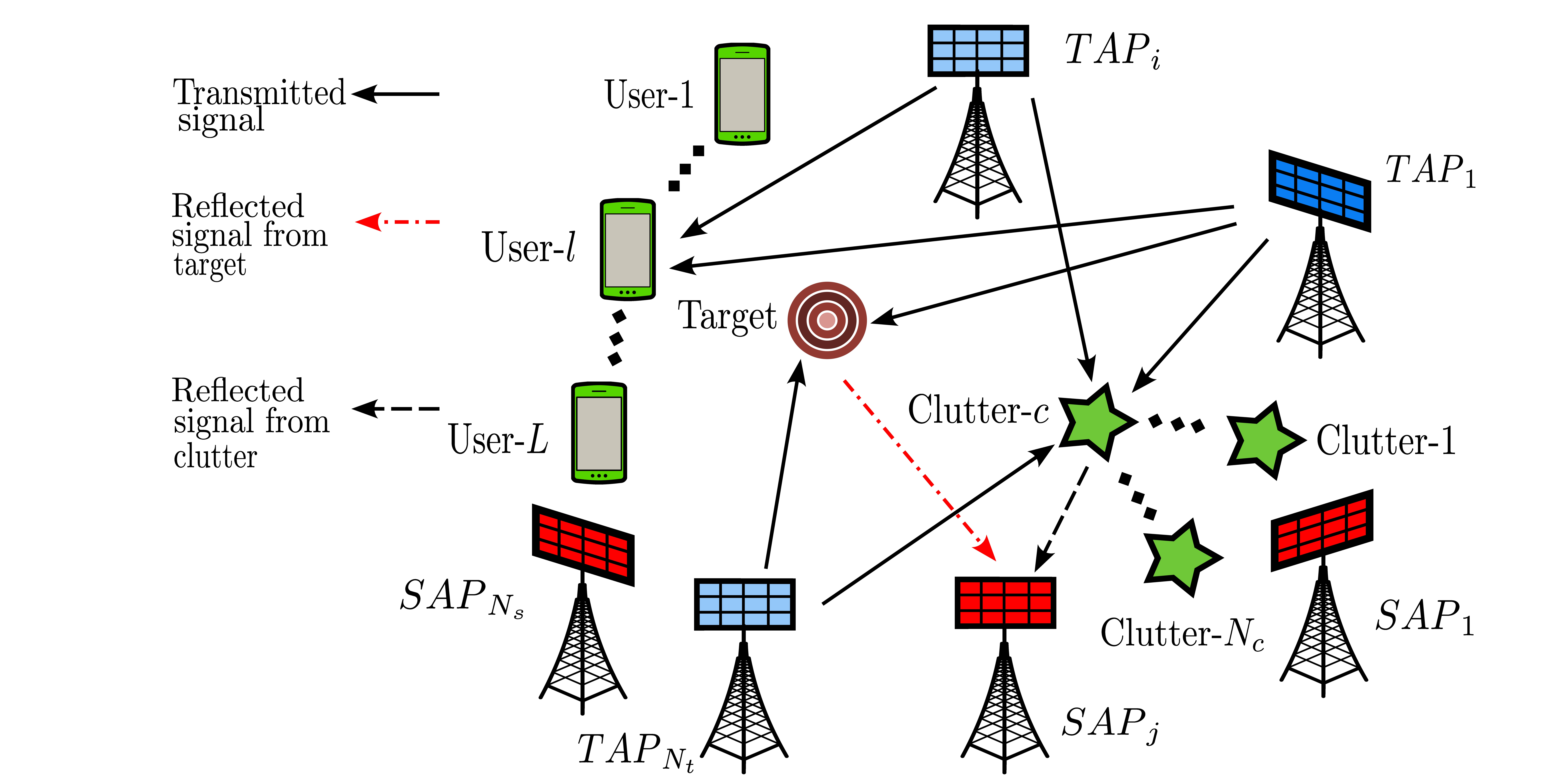
System model
Network comprises \(N_t\) distributed \(M_T\) antenna transmit APs and \(N_s\) \(M_R\)-antenna sensing APs jointly serving LLL single-antenna users and one target in the presence of \(N_c\) clutter sources; arrays are uniform rectangular planar.
Communication channels follow spatially correlated Rician fading; sensing links are LoS.
Performance metrics & analysis
Communication: closed-form user rate expressions.
Sensing: average SCNR and MUSIC spectrum peaks for localization.
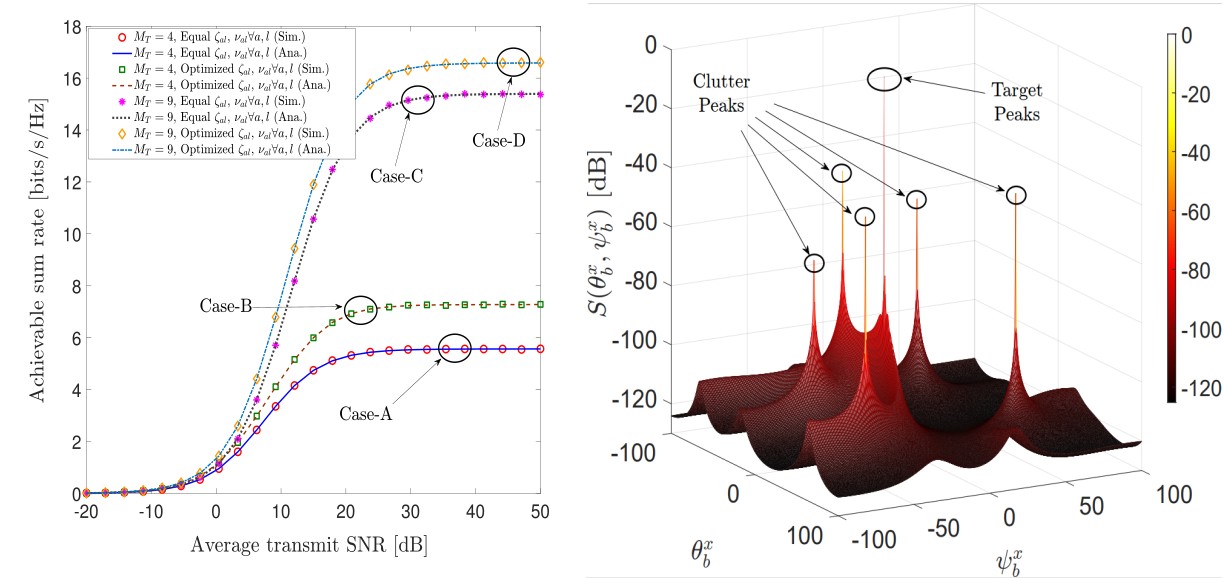
Key numerical findings
With \(M_T=4\), optimized power control boosts system-wide sum rate over equal-power baseline.
Increasing AP array antenna count and yields additional sum-rate gains
MUSIC spectrum successfully distinguishes one target and five clutters at the configured azimuth/elevation angles, validating sensing functionality.
 |
Conclusion
Demonstrates that simple, locally computed conjugate precoders plus statistical power optimization can deliver robust joint communication-and-sensing in large cell-free deployments without heavy CSI exchange, marking a practical step toward scalable 6G ISAC networks.
Future work - Learning-based Cell-Free Massive MIMO-aided ISAC
System model and channel model:
- The system comprises multiple transmit APs, multiple receive APs, multiple users, multiple clutters, and a single target.
- Channels are modeled using spatially correlated Rician fading with path loss effects.
Objective: Downlink beamforming optimization for superimposed ISAC waveform design
The beamforming design problem is formulated under three distinct optimization goals:
01) Sensing-Centric Design:
- Objective:Maximize the sensing sum rate.
- Subject to: A total transmit power constraint and a minimum required communication rate for each user
02) Communication-Centric Design:
- Objective:Maximize the communication sum rate.
- Subject to: A total transmit power constraint and a minimum required sensing rate at each receive AP.
03) Joint Design:
- Maximize the weighted sum of the communication sum rate and sensing sum rate.
- Subject to: A total transmit power constraint.
Solution Approaches:
Each of the three optimization problems is addressed using the following methods:
Conventional Optimization Techniques:
Convex-concave procedure algorithm (CCPA)
Manifold optimization (MO)
Data-Driven Approach:
A deep learning-based solution is developed and trained to approximate the optimal beamforming design.
The performance of the deep learning method is compared against:
The two conventional optimization approaches (CCPA and MO)
Traditional linear precoding techniques, such as maximum ratio transmission (MRT)
References
1. Kulathunga, J. K. Dassanayake, and G. Amarasuriya, “Cell-Free Massive MIMO-Aided ISAC,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Commun. (ICC), Montreal, Canada, Jun. 2025.