Unsupervised learning-Based ISAC Waveforms
System Model
 |
Motivation
Classical ISAC waveform design via optimization becomes computationally prohibitive as array dimensions grow and must navigate inherent sensing - communication trade-offs.
Core contribution
We propose an unsupervised learning - based ISAC waveform design that embeds the sensing-communication trade-off in a custom loss function and enforces constraints through a Lambda layer, providing a practical alternative to model-driven methods. Performance is benchmarked using achievable rate, probability of detection (PD), and Cram\(\acute{\text{e}}\)r - Rao bound (CRB).
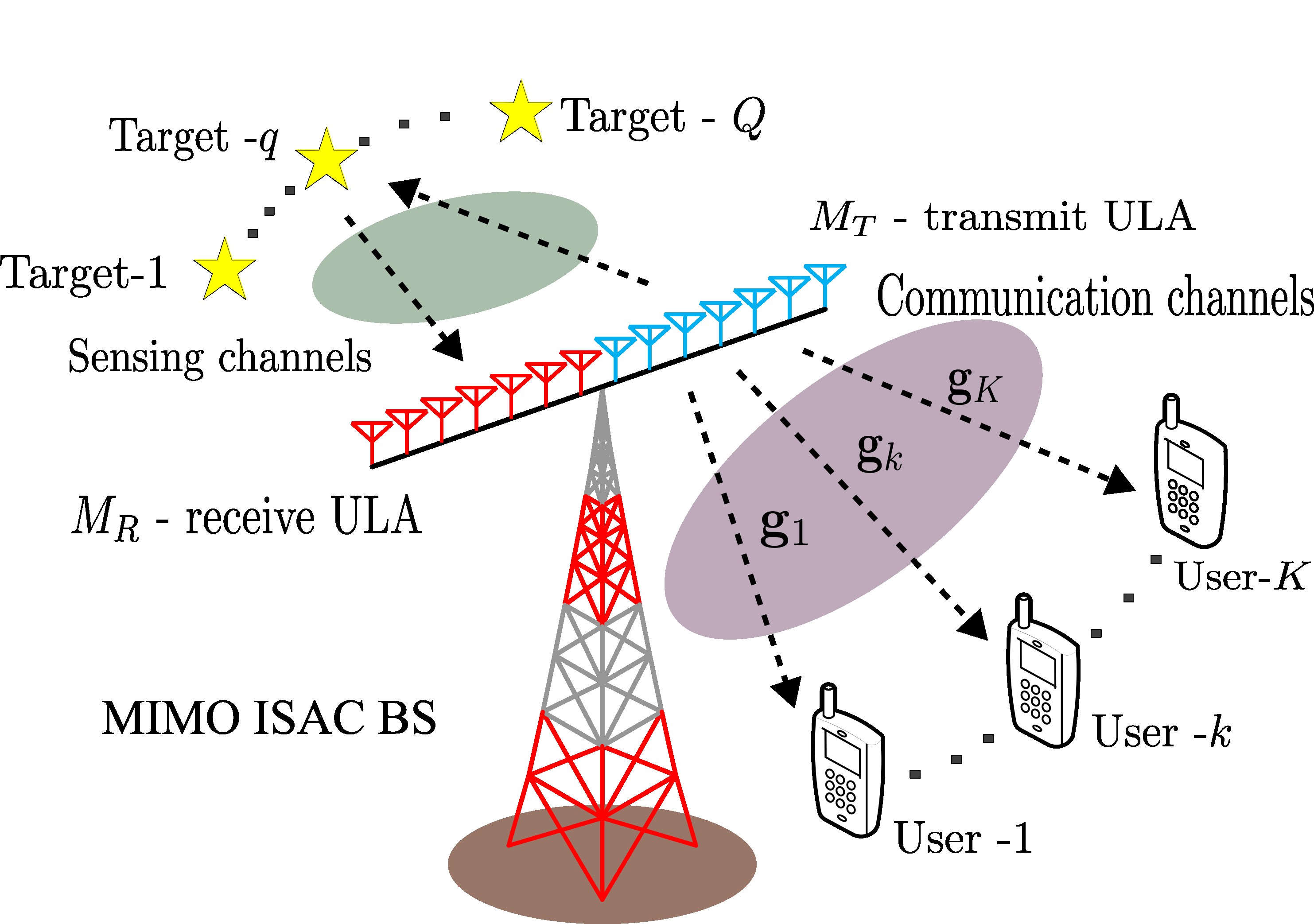
System model
A dual-functional MIMO BS with separate transmit/receive ULAs serves \(K\) single-antenna users while probing \(Q\) targets; full-duplex loop interference is assumed negligible due to modern cancellation techniques.
ISAC waveform designs
(i) Baseline: A trade-off between multi user interference (MUI) of the communication users and the mismatch between the designed and reference ISAC waveforms are jointly considered.
(ii) Learning-based: A trade-off between MUI and the mismatch and mean square cross-correlation of transmit beampatterns are considered. This sensing loss is tailored to multi-target detection. This problem is non-convex, and hence, we resort to a learning-based approach.
Overview of ANN architecture
A fully connected network with batch normalization before each hidden layer; ReLU activations in early hidden layers and Tanh in the final hidden layer; the Lambda output layer enforces the total-power constraint. Inputs comprise stacked real/imaginary parts of the channel matrix and desired symbol matrix; outputs map to the ISAC waveform entries.
 |
Training protocol (Offline) & implementation
Unlabeled dataset generated via Monte Carlo (channels) and QPSK symbols; trained with Adam, mini-batches, and early stopping; implemented in PyTorch. A large-scale dataset with 60\(/\)20\(/\)20% traintestpredict split and typical hyperparameters is reported.
Computational complexity (Order-level)
Proposed method scales as \(\mathcal{O}(K M^2_T \tau_d + K M_T \tau^2_d)\), substantially lower than a conventional SDR baseline \(\mathcal{O}((M_T \tau_d)^{3.5})\)
Numerical results
We provide three main numerical results to analyze the performance of the proposed learning-based algorithm compared to classical optimization techniques.
Sum-rate
Rate-detection trade-off
CRB-rate trade-off
 |
Conclusion
Although sub-optimal, the unsupervised approach achieves comparable performance with significantly lower complexity, and is thus attractive
for large-array 6G ISAC implementations and real-time deployment.
The full-published version of this work can be found here.
References
1. J. K. Dassanayake, R. Kulathunga, G. A. A. Baduge and M. Vaezi, “Unsupervised Learning-Based ISAC Waveforms”, in IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 14, no. 9, pp. 2663-2667, Sept. 2025.