|
Laboratory 6
Aim: To design and implement a
circuit which detects errors in a serial data transmission line.
Material needed: Protoboard,
Logic template, 74175 DFlip-Flops and 74157 Quad
2-to-1 MUXes, one EPROM chip, 2 SPDT switches, a
DIP switches, a set of resistors (0.25W, 1k ohms and 0.25W, 330 ohms),
LED's, segment display AND, OR and NAND gates and wires for Protoboard.
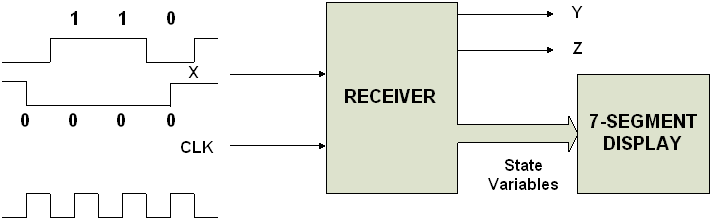
Problem: your goal is to design and
implement a receiver circuit which has a clock and a serial data input line
x. The following bit sequences are known to be erroneous.
1.
Four consecutive 0's.
2.
Two consecutive 1's followed by a 0.
Your circuit should
check for these sequences and set an output line Y to indicate an error.
Let the initial state be all the zero state, which can be forced using
lines of the D-FF's. Since some states of the
machine may be unused and random noise can send the machine to one of these
states, we need to make sure that even if the machine goes to unused state,
it can return to a valid state. To implement this let there be a transition
from each unused state to the initial state. At the same time set another
output line z to indicate that the machine was in an unused state due to
noise.
In our case, we can
simulate a noisy environment by parallel loading (PL) an unused state onto
the FF's. The PL circuit can be constructed using
MUXes. Both clock and input X need to be debounced. The input x and outputs y and z should be
displayed on LED's and the state of the machine should be displayed on a
7-segment display.
Prelab:
1.
Design the circuit and draw its diagram.
2.
Draw a schematic diagram using chips (include pin numbers, Vcc and ground).
3.
Generate a set of test inputs that would check the operation of
the register. What is the minimum number of clock cycles required to test
it completely.
Demo: Build the circuit and
demonstrate its operation by applying different input combinations.
1.
Derive inputs to the circuits using DIP switches and the outputs
to LED's.
2.
Apply your test input set and demonstrate the operation.
Note: Use two D-FFs
to latch your output signal Y and Z.
|